Reverse Engineering
Redesign models and replicate mechanical parts
What is Reverse Engineering
Reverse Engineering is the process that allows you to digitize a physical object by laser scanning, processed with 3D modeling software. This process, thanks to an in-depth analysis of the operation, design and development phases of an object, allows you to create a copy that has the same characteristics or a variant to which improvements have been applied that allow you to remedy previous design errors.
With the Reverse Engineering process, also called “back engineering”, we literally mean a reverse engineering process, or a design method where the team of engineers works to obtain all the information of the initial project starting from the final result.

Innovative solutions in industrial design
When to use Reverse Engineering
This type of innovative design is particularly useful when you do not have the complete original documentation with the related technical drawings, or if you do not have complete information on the engineering of an object.
Reverse Engineering is a valid alternative, even in the event that spare parts are no longer available on the market, either because they are out of production or because the manufacturer may have ceased to operate.
Reverse Engineering can also be very valuable to insert new elements into a product, to improve a defective part or to rebuild parts that have been created by hand.
This technology is used to optimize the production phases, reducing waste, thanks to the ability to generate prototypes absolutely faithful to the original at low cost.
Thanks to Reverse Engineering it is also possible to build a digital archive of the various parts or spare parts, in order to keep the information for future processing.
Optimization of production times and costs
Advantages of Reverse Engineering
Thanks to this innovative technology it is possible to:
- Speed up the product design process
- Reduce the time and cost of producing products
- Analyze existing product designs and increase their performance
- Reproduce spare parts and products, correcting any defects
- Produce spare parts and parts without purchasing them from an OEM which could take a long time and high costs
- Produce spare parts and parts out of production and therefore no longer purchasable on the market.
- Perform proactive maintenance on critical components by anticipating their breakdown, creating a spare parts inventory and reducing unexpected downtime.
Sectors of application of Reverse Engineering
3D reconstruction through Reverse Engineering has a wide field of application, which we could define as almost unlimited. Among the main sectors in which it is used we find the industrial, mechanical, aeronautical, aerospace, automotive, civil, architectural, medical and sculptural sectors.
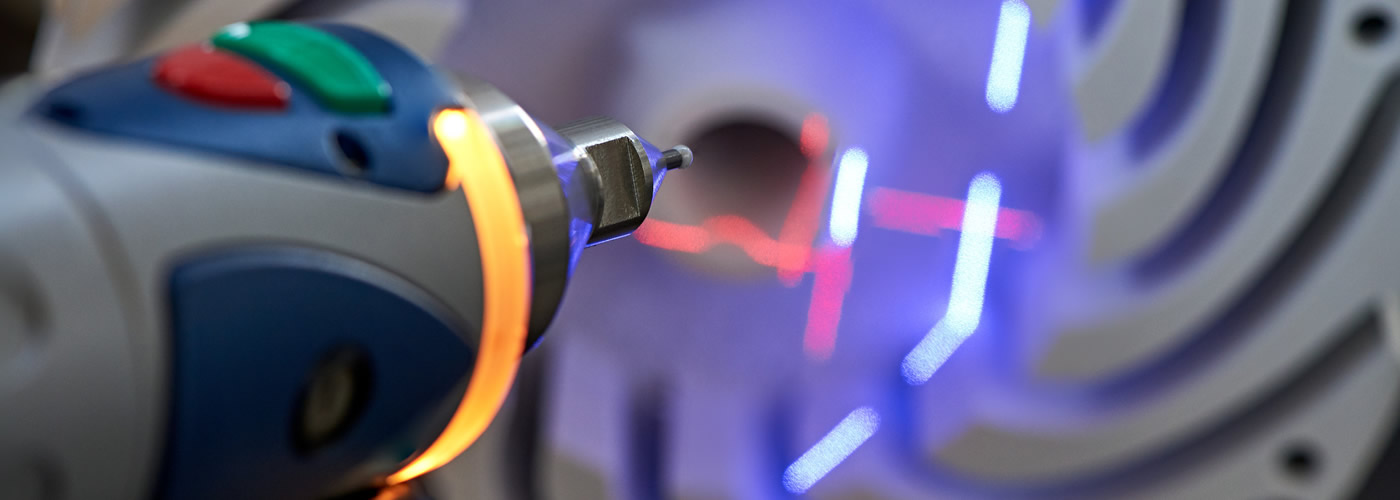

Prototypes ready in no time
Reverse Engineering processing phases
In the field of design, the term Reverse Engineering summarizes the entire 3D digitization process of a physical object, in order to carry out its analysis or remodeling on a computer, through the use of specific software.
Before starting a Reverse Engineering project, it is necessary to understand exactly what your needs are and the objectives to be achieved; subsequently it will be necessary to choose the 3D measurement technology to be used based on the application and data acquisition environment.
The reverse engineering processing procedure can be carried out with different techniques and software, based on specific final needs, the types used are:
- 3D parametric reconstruction: the final file is made up of fittings, planes, curves and cylinders recognizable by the various CAD software.
- 3D reconstruction for exact surfaces: the file consists of a series of surfaces that are “placed” on the scan as if it were a “skin”. This system is best indicated when the shapes are called “organic”.
The Reverse Engineering process consists of these phases:
- 3D scan
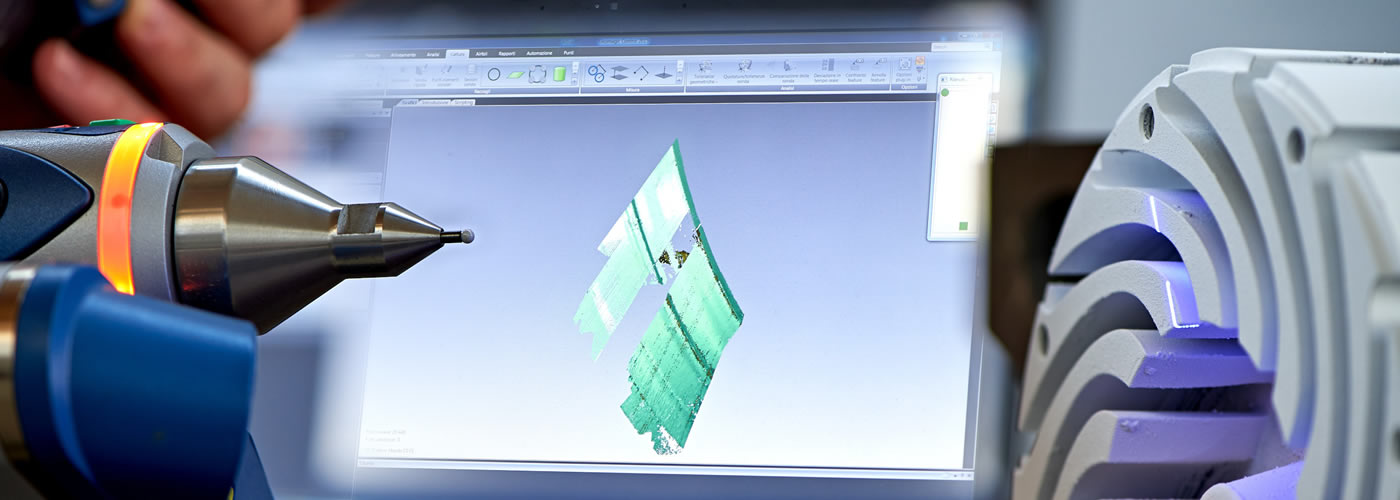
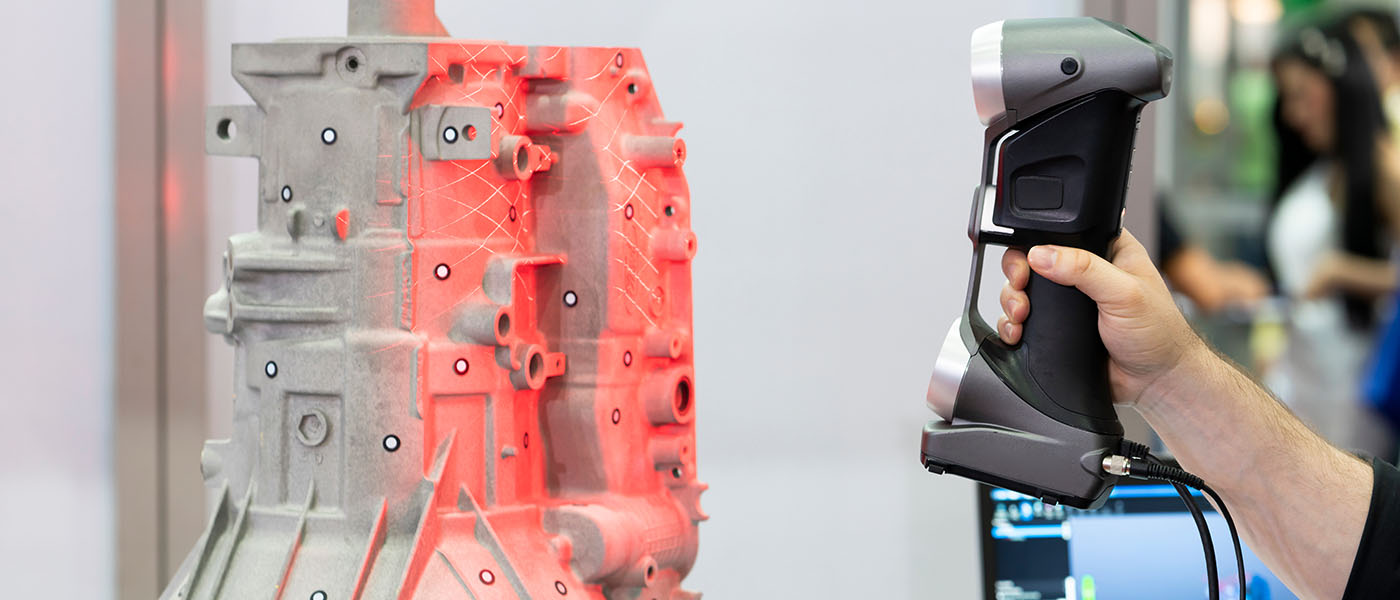
The first phase of Reverse Engineering consists in carrying out a three-dimensional scan of the object to be reproduced; through a video projector the object is completely enveloped by a sequence of encoded light patterns, simultaneously, two cameras photograph it at each moment of the sequence or by means of fixed or mobile laser scanners. This process is identified as 3D scanning.
Subsequently, through a specific software, the triangulation of the points is performed, that is the reconstruction of the position of all the acquired points that make up the object and that generates the mesh; the higher the density of the detected points, the better the approximation of the mesh will be. - Mesh optimization
Once the triangular mesh has been obtained with the 3D scanner, the next step is carried out manually by an operator, who, using software, transforms the triangular mesh just obtained into a quadrangular one, optimizing it for the following steps through a possible removal of isolated points, the elimination of noise and irregular areas and closing of unwanted holes, all while maintaining the original shape and size of the object. - Corrections and changes
After optimization, the mesh is re-examined to make further corrections and changes due to errors during the scanning of the object, always through the use of specific CAD software. - Identification of mathematics
The last phase of reverse engineering consists in identifying the “mathematics” of the model obtained or all the information needed to reconstruct the mathematical model of the project. These mathematics will be used to generate the molds with which to make the new object.
Acquisition of millions of points per second
General conclusions
The 3D measurement technology makes it possible to significantly speed up the Reverse Engineering process; 3D scanners are in fact quite versatile to use allowing to acquire the scan of the piece directly in the production environments, thus avoiding the customer to ship it to the laboratory.
Through 3D scanners you can acquire millions of data points per second, obtaining a mesh in no time. These tools have a high accuracy even with complex geometries or surface representations of the object, thus avoiding the human errors often present in manual measurements, which lead to longer and more complex production times.
The importance of reverse engineering in the production of industrial spare parts is an indisputable element that offers unprecedented innovation in the management and maintenance of industrial machines.
Thanks to Reverse Engineering it is possible to optimize workflows making them more efficient and sophisticated, create new solutions, improve production processes and increase profits.


